A cloud strategy document is used to identify, capture and define how the business vision, strategy, goals and values are supported and delivered by cloud IT services.
The strategy document is also used to guide the business in the selection and application of cloud IT services.
To select and effectively utilise cloud services Astute recommends businesses start by creating and using a cloud strategy.
In this series Astute presents a seven step template approach that customer centric businesses use to define their cloud IT strategy.
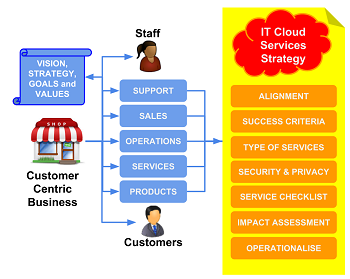
The cloud IT strategy template structure is as follows:
- Alignment. How the vision, strategy, goals of the business are supported by the use of cloud services.
- Success criteria. Used to measure and determine whether the cloud service implementation has been successful (or not).
- Types of service. Identifies and describes the types of cloud IT services the business should (and should not) use.
- Security and privacy. Identifies and defines cloud IT services security and privacy criteria.
- Service checklist. Criteria used to compare and select the cloud service or application providers.
- Impact assessment. Changes to business operations as a result of selecting the cloud service or application
- Operationalise. How to introduce and use the selected cloud services in business IT operations
The alignment section of the template strategy defines how the business vision, strategy, goals and values are supported by the use of cloud IT services. The content of the section is developed by providing concise responses to each of the following questions:
1. Business challenges and benefits when using cloud IT services?
Consider:
- Capability and convenience; easy to subscribe, pay and access.
- Vast range of services available (e.g. email, storage, accounting, sales and marketing etc).
- Operate using a range of devices (i.e. computer, tablet, smart phone).
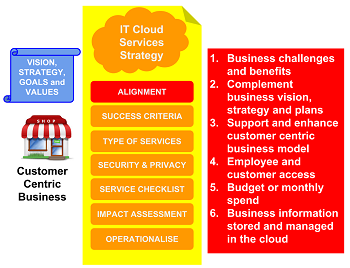
2. How do cloud services align and complement the business vision, strategy and plans?
Consider:
- Leverage existing cloud services to deliver and support company products.
- Agility - ability to adjust and update products and service offerings by adding or changing cloud service providers.
- Reduced and lean (capital) operating costs; better cash-flow management.
3. How does cloud support and enhance a customer centric business model?
Consider:
- Customer ease of access and flexibility.
- Customer provisioning, billing, support and feedback services.
4. How will employees and customers access the cloud service?
Consider:
- Identify the locations and scenarios that describe how customers and employees will access services.
- Describe how employees and customers are provisioned to access the cloud services.
- Identify how customers and employees access the services. E.g. computer, smart phone, tablet etc.
5. What is the budget / monthly spend for the service?
Consider:
- Identify the type of cloud IT service plan. Cloud service plans can be priced per user (or groups of users) per month or per user per annum (usually discounted rate per user per month over 12 months).
- Document and budget for monthly or annual cloud IT service costs in business financial planning.
- Cloud IT services can be charged using foreign currency rates. If this a significant amount Astute recommend that business investigate and apply methods to reduce foreign exchange rate risk.
6. What business and customer information can be stored and managed in the cloud?
Consider:
- Locate or define an information classification policy for the business. Astute recommends using a ISO standards compliant classification model (e.g the ISO27001 classification template).
- Ensure the policy defines the classification of information can and cannot be stored and accessed from the cloud.
- Identify the types of information you want stored and accessed from the cloud (e.g. customer name, address, email, phone number, account details etc).
- Assign an information classification (from the policy above) to each of the types of information identified.
- Using the policy, list the types of information (based on information classification) that can and cannot be stored and managed in the cloud.
In our next article Astute will describe how to develop and create content for the Success criteria section of a business cloud IT strategy.
The success criteria section of the cloud IT services strategy template identifies the processes and data used to determine the success (or failure) of a cloud service; quantifying how the service:
- Improves customer acquisition, experience and satisfaction.
- Improves employee experience and satisfaction.
- Delivers operational efficiencies to the business.
- Operates within the allocated financial budget.
- Is procured and cancelled.
Cloud IT service success is determined using cloud service costs, and customer and employee benefits; measured and reported using the following six criteria.

1. Customer acquisition, experience and satisfaction
Collect, measure and report on the following customer data before and after the introduction of the cloud service:
- Number of customers.
- Average income (to the business) per customer.
- Customers acquired.
- Customers lost.
- Customer retention benefit or loss. I.e. Subtract the customers lost from customers acquired then multiply the result by the average income per customer.
- Customer satisfaction survey results (i.e. Do customers feel better or worse off as a result of using the IT cloud service?).
2. Employee experience and satisfaction.
Collect, measure and report on the following customer data before and after the introduction of the cloud service:
- The number of employees are using the service.
- The number of employees (using the service) that find the service easy to use (ie are satisfied with the service).
- Overall employee satisfaction with the service (e.g. 7 out of 10 employees using the service and find the cloud service easy to use; satisfaction of 70%).
- Employee identified problems or issues that need to be resolved to improve the use of the service.
- Estimated costs (time and materials) to rectify employee identified problems or issues with the service.
3. Operational improvements and efficiencies
Collect, measure and report on the following customer data before and after the introduction of the cloud service:
- Operational improvements or efficiencies have been identified as a result of introducing the service (e.g. improvements on-boarding new employees, reduced operating costs).
- Savings (time and materials) to the business as a result of the operational improvements or efficiencies.
- Problems and inefficiencies identified as a result of using the service.
- Operational changes required to remedy the identified problems and issues.
- Costs (time and materials) of implementing the operational changes to remedy the identified problems and issues.
- Overall operational benefit or cost of the service (i.e. subtract the costs from the savings).
- Risk position. How risks to the business have been addressed by the use of the service. E.g. Improved customer and business security, information backup and retrieval, enhanced ability to deliver mobile access to services etc.
4. Business product (including services) enhancements
Collect, measure and report on the following customer data before and after the introduction of the cloud service:
- Operational improvements or efficiencies in the delivery and support of the business products (e.g. Improvements to configure and add new customers to the product and service).
- Savings (time and materials) in the delivery and support of the business products.
- Number of support calls and complaints.
- Number of support calls and complaints specifically regarding the cloud service.
- Costs (time and effort) of managing and resolving support calls and complaints specifically regarding the cloud service.
- Overall business products and service benefit; support call volumes versus service benefits (subtract the costs from the savings)
5. Service operating budget
Using the charges and data collected above determine the financial viability of the cloud IT services (for the specified period) as follows:
- Estimated (budgeted) costs of the cloud IT service.
- The actual cost of the cloud IT service (i.e. includes any additional data, storage or usage fees).
- Cloud IT service benefit or cost (subtract actual costs from estimated costs).
- Customer retention benefit or loss from the customer satisfaction survey results collected in criterion 1.
- Costs to rectify employee identified problems from criterion 2 above.
- Operational benefit or cost of the service from criterion 3 above.
- Business product benefit or cost from criterion 4 above
- Overall financial benefit or cost of the cloud IT service by considering all of the above. Remember a positive value is a benefit; a negative is a cost.
6. Retain or cancel the service
Consider what has been collected and calculated. I.e:
- Customer satisfaction.
- Employee satisfaction.
- Business risk position.
- Financial benefit or cost of the cloud IT service.
The results collected from criteria 6 above are "weighted" by the business and used in the decision to retain or cancel the cloud IT service. E.g: Criteria used to retain the service could be:
- Customer satisfaction is at the same rate (as the previous period) or better and
- Employee satisfactions is at the same rate or better and
- Business risk position is the same (i.e. has not got worse) or better and
- There is a financial benefit - or the cost of the service is acceptable - to the business.
In our next article Astute will describe how to develop and create content for the Services criteria section of a business cloud IT strategy.
The types of services section of the Astute cloud IT services strategy template is used to identify and select one or more of the three cloud IT service model and deployment types:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Provides access to networking features, computers (virtual or on dedicated hardware), and file storage space; appeals to businesses that want to extend infrastructure capacity without spending capital.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS). Used to develop, host and operate applications; removing the need for businesses to manage the underlying infrastructure (usually hardware and operating systems) and focus on the development and management the application.
- Software as a Service (SaaS). Provides access to applications that are developed and managed by a (cloud) service providers. The business does not have to develop applications or manage infrastructure.
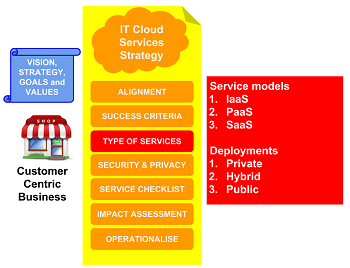
There are also three common cloud deployment options for each of the above cloud service models:
- Private cloud. Used by business to deploy infrastructure and applications on-premises or in dedicated data centers that provide internet accessible services to customers and employees. Private cloud deployments typically use server virtualisation technology as well as resource and performance management tools.
- Hybrid. Used by business to connect infrastructure and applications between public cloud services and on-premise (or private cloud) infrastructure and applications.
- Public cloud or (just) cloud. No business owned or deployed infrastructure or applications; service configured, operated and managed by a third-party provider; managed by the business.
Cloud models and deployment types are then combined to deliver different types of services. E.g:
- Cloud SaaS for document storage (e.g. Google Drive, Dropbox, Microsoft One Drive etc).
- Cloud SaaS for office documents (e.g. Google Docs, Microsoft Office 365 etc).
- Hybrid SaaS for enterprise solutions (e.g. SAP Human Resources integrated with on-premises MS Active Directory - ensures users login to the SAP application using business allocated user names and passwords.
- Private cloud for business information backup and archiving (e.g. backup and archive of Cloud SaaS information).
What cloud deployment type and service model should my business use?
The table below is used to select cloud IT service model and deployment type based on the business capability and environment.
| Business situation | Deployment type | Service Model |
|---|---|---|
| No existing IT infrastructure; do not develop applications | Cloud | SaaS |
| Have existing IT infrastructure and application licenses | Private | N/A |
| No existing IT infrastructure and application licenses | Cloud | IaaS |
| Existing IT services capacity (e.g. Directory services via Active Directory) | Hybrid | SaaS |
| Developing applications and no existing IT infrastructure | Cloud | PaaS |
| Developing application and existing IT infrastructure | Private or Hybrid | N/A |
The cloud deployment type and service model, once selected, is factored in to the service operating budget for the success and privacy section of a business cloud IT strategy.
In our next article Astute will describe how to develop and create content for the security and privacy section of a business cloud IT strategy.
The security and privacy section of the Astute cloud IT services strategy template describes an approach to ensure that information stored (by the business) in the cloud remains safe, secure and private.
Astute's approach to cloud security and privacy is based the businesses accepting responsibility and accountability for ensuring customer and business information stored in the cloud is safe, secure and private.
"Private" includes ensuring information privacy concerns are considered whenever personally identifiable or other sensitive information is used in a cloud service.

A responsible and accountable approach to cloud security and privacy helps a business to:
- Understand the nature and purpose of the information used in the service.
- Identify the risks (to the business) in managing the information used in the service.
- Identify and specify technologies and processes that should be used by cloud service providers.
- Assess cloud service provider offerings; ultimately selecting a cloud service.
How do I determine what information I can store in the cloud to keep it secure, safe and private?
The following five step approach is used by business to ensure information stored in the cloud is safe, secure and private:
- Identify, define and classify all the information that can (and cannot) be stored in the cloud service.
- Identify the legal and regulatory conditions that apply to the collection and use of information used by the cloud service, especially personal information.
- Identify risks and impacts to the business when failing to keep the information stored in the cloud secure and private.
- Mitigate business risks and impacts (step 3) by identifying and specifying "controls", processes and technologies, to be applied to the use and access of information stored in the cloud.
- Evaluate potential cloud service offerings by verifying the cloud provider implements equivalent controls (step 4) to mitigate the business risks and impacts (step 3).
Astute's Offer is also available to businesses to assist in the determination of what information can be stored in the cloud and to keep the information secure, safe and private.
In our next article Astute will describe checklist of a business cloud IT strategy.
A service checklist, created from the Astute cloud IT services strategy template, is used by businesses to compare and select cloud IT service provider(s). The service checklist:
- Lists the features and functions of a cloud IT service that are needed to meet (business) outcomes and objectives.
- Lists the security controls needed to protect employee and customer data in the service.
- Compares the features, functions and security controls of multiple cloud IT service providers.
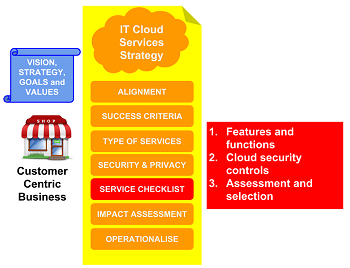
The comparison is then used to support the selection of an IT cloud service provider. Astute recommends collating and preparing the data for review in the cloud services assessment and comparison checklist presented below. Checklist column descriptions (#1 to #4):
- The template content used for the check list.
- Text description of the feature used for the comparison.
- Yes / No result indicating whether the feature or function is supported by the cloud provider.
- Information used to support the "Meets Yes" result (e.g. web site URL, brochure page, email, or comment)
Cloud services assessment and comparison checklist
| #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Per cloud services provider | |||
| Source | Feature description | Meets (Y/N) | How (evidence) |
| Alignment | Feature X (identified by the business to improve customer service) | ||
| Feature Y (identified by the business to improve customer service) | |||
| Cloud service supports employee access from a range of devices (i.e. computer, tablet, smart phone etc) | |||
| Cloud service supports storage and retrieval of customer information (e.g. name, address, contact email, phone) | |||
| Success criteria | Cloud service provides data to measure customer acquisition, experience and satisfaction. | ||
| Cloud service supports or provides access to data used to measure business operational improvements and efficiencies. | |||
| Cloud service usage fees and charges are within the allocated service budget. | |||
| Cloud service termination fees and charges are well explained and documented. | |||
| Services types | Cloud service supports the specified business cloud IT service model and cloud deployment option. | ||
| Service model - IaaS / PaaS / SaaS | |||
| Cloud deployment - Private / hybrid / public cloud | |||
| Security and privacy | Cloud service provides the "controls" required to ensure that specified business information is safe, secure and private. | ||
| Cloud service provides the "controls" required to support any legal and regulatory conditions that apply to the collection and use of information used by the cloud service, especially personal information. | |||
| Cloud service provider demonstrates compliance to cloud information security and privacy standards (e.g ISO 27001 or Cloud Security Alliance - Cloud Controls Matrix etc) | |||
| Provides evidence of compliance ISO 27001 information security standards by supplying copies (to the business) of recent audits performed on the cloud service in accordance with ISAE 3402 and SOC 2 standards. | |||
Once completed the service checklist provides the business with a "side by side" comparison of cloud service provider offerings, as well as identifying a preferred cloud service provider.
Adopting and operating a cloud IT service will require changes (or create impacts) to business products, services and operations. In our next article Astute will describe approach business use to identify (and resolve) business impacts introduced as adopting and operating a cloud IT service.
An impact assessment is used in the Astute cloud IT services strategy template to identify and address impacts to business operations, products and services by using the selected cloud service.
Astute recommends a four step approach to identify and address any business impacts introduced by the Checklist template component:
- Review the results of the cloud service features and functions assessment. An impact exists where the service meets result is NO.
- Review the results of the security and privacy assessment (per classification). An impact also exists where the service meets result is NO.
- Review the cloud service online documentation, especially the how-to guides. An impact exists where the use of the cloud service conflicts with the way the business is structured or operates.
- Identify and apply remedial actions to reduce (or remove) each of the identified impacts. The table below lists common impacts (and typical remedial actions) for businesses adopting a cloud service.
Common impacts and remedial actions
| Impact | Remedial actions | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Who in the business (employee, manager, unit or group) is responsible for the operation and internal support of the cloud service | Change the business structure (roles, responsibilities, reporting lines, processes etc) to ensure responsibility and accountability for internal support of the cloud service | Typical approach is for the business to adopt (or replicate) the same operations or processes used by the cloud service provider |
| Includes cloud service support, access and permissions management (e.g. administrators, user access, approvers etc) | ||
| How to ensure that sufficiently trained business teams (employees) are available to support introduction and operation (including service level agreements)of the new service or product? | Employee training, including dry-runs of new processes introduced to the operate the service | Typical approach is for the business to rollout a new (cloud) service to a "pilot" group of users. This allows business to identify, refine and resolve any "glitches" with the delivery and operations of the service |
| Customer experience and support service level agreements meet or exceed current service level agreements | Service rollout strategy that outlines the approach (sales, marketing etc) to ensure the successful launch and adoption of the new cloud service | Again using the rollout a new (cloud) service to a "pilot" group of users approach |
| Identify and use updated or new customer engagement channels and technologies | Customer support provided by toll-free phone, online chat, support portals and social media | |
| How to ensure that customers (and employees) are aware of changes to the service; including outages required to transition the service | Communications strategy or plan that outlines activities, significant dates, approaches to advise customers and customers, content and media used to communicate the changes | Approaches outlined in the communications plan include phone, targeted email, web site and social media, in-application reminders, conference and online meet-ups |
| How to deal with "feature gaps or omissions"? Where the feature required is not provided or supported by the selected cloud service | Review and adapt the the business structure (roles, responsibilities, reporting lines etc) to address the gap | Business either adopts the same operations or processes used by the cloud service or implements a business specific workaround |
| Review and apply cloud service configuration options to address the feature gap | ||
| How to apply one or more specified security and privacy controls that are not provided by the cloud service | Source (locate) another technology or cloud solution to provide the control. Integrate this with the selected cloud service | E.g. "as a service technology controls" such as intrusion detection prevention as a service, firewall as a service, identity as a service etc |
In our next article Astute will describe operations of a business cloud IT strategy.
The final step in the Astute cloud IT services strategy template is for businesses to operate the selected cloud service; ensuring the service delivers products and services to the business and customers of the business.
When operating cloud services Astute recommends that business periodically (e.g. monthly, bi-monthly or quarterly) re-use and re-apply approaches and concepts from their developed cloud strategy template to ensure:
- Specified success criteria is still being met by the service; especially, customer acquisition, customer and employee experience and satisfaction, service charges are within the specified service operating budget and criteria defined to retain the service is still being met.
- The cloud service information classification and conditions have not changed.
- The cloud service provider is continuing to offer the service using the identified and specified security controls, risk mitigations (controls) as supported by the service evaluation and checklist.
- Remedial actions, implemented by the service provider, are continuing to reduce or remove identified impacts to business operations, products and services.
This article concludes Astute's series on developing a business cloud IT strategy. We hope you have found the series helpful.
In our next article Astute will describe Astute Offer of a business cloud IT strategy.
Astute's free and with no obligation consultation offer allows businesses to take advantage of our services and mobile and cloud applications capabilities to:
- Perform business data security and privacy assessments to identify what information the business can store in the cloud and to keep the information secure, safe and private.
- Perform impact assessments to identify and resolve any "feature gaps or omissions" between the business processes and its nominated cloud service providers.
- Review and determine whether the business goals are being met and supported by their technology.
- Investigate a current technology issue or provide advice on a upgrade or expansion.
- Develop and support mobile applications for the business.
- Assist in the comparison and selection of cloud products and services that assist owners to overcome challenges experienced when operating a micro-businesses.
To take advantage of our offer simply register for the Astute free and no obligation mobile and cloud consultation .